WHAT IS MUTUAL FUND

A mutual fund is ”pool of funds from large number of investors,who have a common investment objective”.It is professionally managed by “fund manager”.The fund manager invests the funds in different securities i.e stocks, bonds, money market instruments & other securities.
The investors,who invests in mutual funds are known as mutual fund” share holders (or) unit holders”.The mutual fund company allots the units to the investors inproportionate to their investment amount.
Mutual funds investment is best way of investment method for,who does not has proper knowledge about stock market.It gives an facility to invests in mutual funds for small investors with just 500/-.
MUTUAL FUND INVESTMENTS
1. LUMPSUM (OR) ONE TIME INVESTMENT :
LUMSUM is the traditional mode of Mutual funds investment. It is best for who has an bulk amount to invest.It gives good returns to the investor in long term period,subject to fund risk.
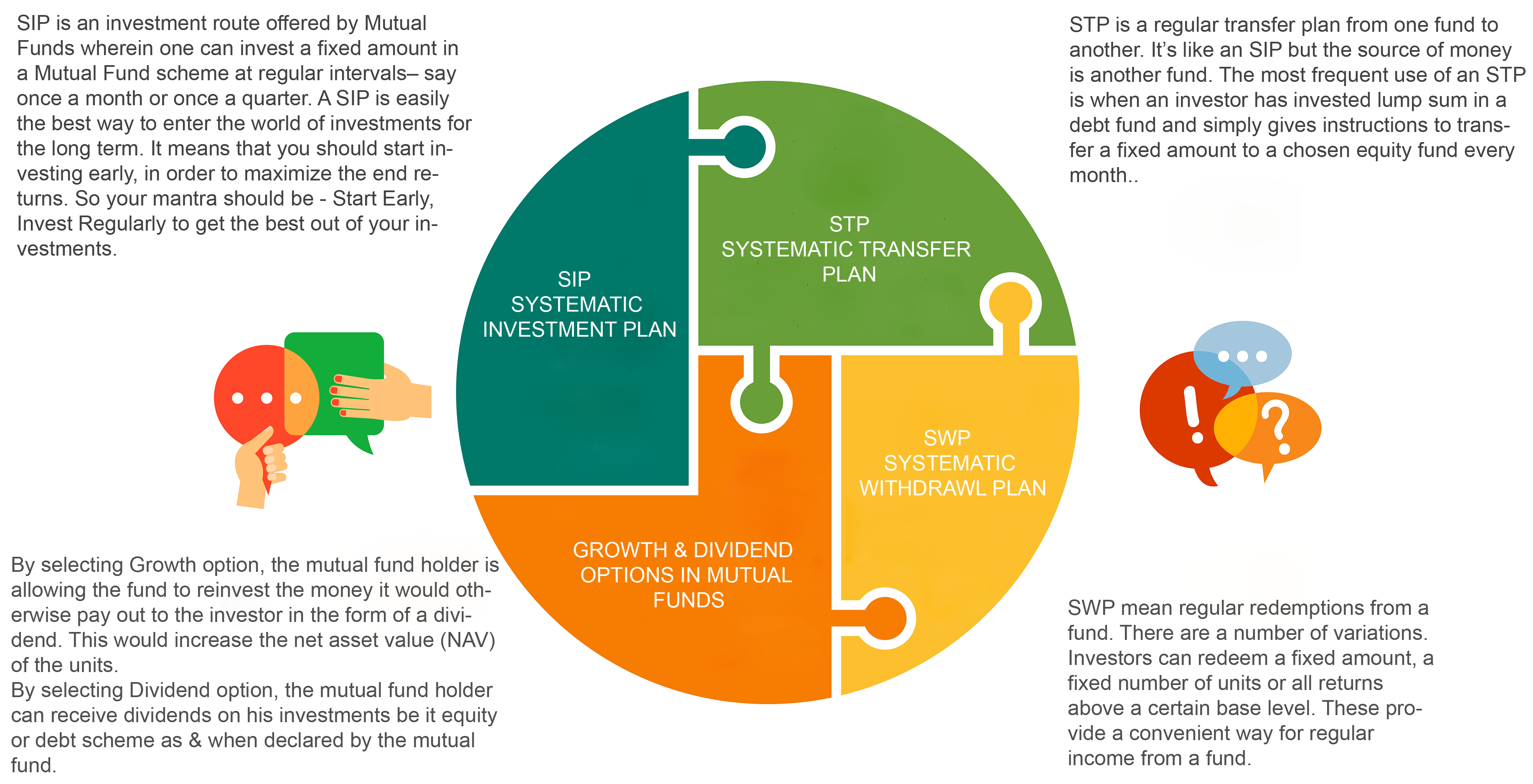
2. SYSTEMATIC INVESTMENT PLAN ( SIP ):
Now a days ,SIP investment is the most popular mode of mutual funds investment.Because we can built an corpus in longterm with systematically invests small amounts regularly.Minimum SIP INVESTMENT is 500/-.
MUTUAL FUND INVESTING vs.DIRECT INVESTING :
- Professional Investment Management
- Risk reduction through diversification
- Convenience
BENEFITS OF INVESTING IN MUTUAL FUNDS
Investing in mutual funds helps an investor in achieving his long term goals by wealth creation. Retirement planning, Tax planning, beating inflation, etc. are the benefits achieved by investing in mutual funds.
TYPE-1 MUTUAL FUND : BASED ON STRUCTURE
These funds buy and sell units on a continuous basis and, hence, allow investors to enter and exit as per their convenience. The units are bought and sold at the net asset value (NAV) declared by the fund.
CLOSE ENDED FUNDSUnlike in open-ended funds, investors cannot buy the units of a closed-ended fund after its NFO period is over. This means that new investors cannot enter, nor can existing investors exit till the term of the scheme ends. However, to provide a platform for investors to exit before the term, the fund houses list their closed-ended schemes on a stock exchange.
INTRERVAL FUNDSInterval funds are basically close ended funds.These funds have features of both open-ended funds and closed-ended funds.these funds open for subscription during certain intervals only.
TYPE-2 MUTUAL FUND : BASED ON INVESTMENT OBJECTIVE
1. EQUITY OR GROWTH FUNDS – These invest in equity & have the potential to generate higher returns in the longer term with some amount of risk. Equity funds are categorized into 7 types namely, Large Cap Funds, Mid Cap Funds, Small Cap Funds, Multi Cap Funds, Sectoral Funds, Thematic Funds, Tax Saving Funds.
2. INCOME OR BOND FUNDS – These invest in Government Securities or Bonds, Commercial Papers and Debentures, Bank Certificates of Deposits and Money Market instruments like Treasury Bills, Commercial Paper, etc. & are relatively safer investments, suitable for Income Generation. Examples would be Liquid, Short Term, Floating Rate, Corporate Debt, Dynamic Bond, Gilt Funds, etc.
3. HYBRID FUNDS – These invest in both Equities and Fixed Income, thus offering the best of both, Growth Potential as well as Income Generation. Examples would be Aggressive Balanced Funds, Conservative Balanced Funds, Pension Plans, Child Plans and Monthly Income Plans, etc.
4. MONEY MARKET FUNDS - These funds invest in short-term fixed income securities i.e. government bonds, treasury bills, bankers’ acceptances, commercial paper and certificate of deposits. These are low risk instruments with low return capability.
5. INDEX FUNDS - These funds invests the funds in index i.e.sensex or Nifty.The performance of the fund depends on the performance of the index. Index funds have lower costs than actively managed mutual funds.
6. SECTORAL FUNDS - These funds invests in particular sector of the market.For example infrastructure funds ,invests in equity shares of infrastructure companies only.The performance of the fund depends on the performance of the respective sector.
7. TAX-SAVING FUNDS - These funds invests the amount in tax-saving instruments,like equity shares.elss is the best example for tax-saving mutual funds.it allows for deduction upto 150000/-p.a.u/s 80c of income tax act-1961.
8. FUND OF FUNDS - These funds invests in other mutual fund schemes.These funds performance depends on performance of those funds.
Benefits of Mutual Funds

Instant and easy diversification:
One tenet of safe investing is to spread your money across different investments. Mutual funds are an easy way to do this. Funds spread money across a large number of investments. You need to be a resident Indian, preferably with a post-office savings bank account.
Professional research and investment management:
There are literally hundreds of companies to track and their prospects could change without warning. Mutual funds employ professional, whole-time investment managers and research staff. Their cost and effort get shared ‘mutually’ among all the investors of a fund.
Convenience:
You can easily make investments and withdraw any amount that you like. Investments can be made by filling up a simple form or by going online with direct debit from your bank account. Similarly, redemptions can be made directly into your bank account within three working days. If you want to directly buy shares to have a diversified set, you will need a lot of money. However, through a mutual fund, you can invest in a diversified set of stocks for far less.
Tax efficiency:
When you buy or sell any investments, you have to pay tax on the profit you make. However, this doesn’t happen when that buying and selling is done on your behalf by a mutual fund. To maximise profits, the fund manager could keep buying and selling stocks as needed, but you have to pay tax only when you redeem your investments from the fund.
Transparent, well-regulated industry:
Mutual funds are obligated by law to release comprehensive data about their operations and investments. Almost all funds release net asset values (NAVs) daily and most release their complete portfolios every month. The SEBI regulates the fund industry very tightly and is constantly refining the applicable rules to protect investors better. Providing access to inaccessible assets: There are many investments that you can make only through a mutual fund. For instance, it’s not easy for individuals to buy government bonds, but they can buy funds that invest in such bonds. While investing directly in foreign stocks could be tricky, you can easily invest in global markets by investing in funds that reside in India but invest in international markets.
SIP, SWP and STP